Pliers have gripped their way through history, evolving from simple bronze-age tools invented to hold hot metal to the indispensable hand tool.
Pliers should not be confused with wrenches. Generally, pliers are designed primarily to grip and manipulate rather than to tighten or loosen nuts and bolts.
List of Pliers

- Fencing Pliers
- Wire Twisting Pliers
- Jewelry Pliers
- Chain Nose Pliers
- Flat Nose Pliers
- Canvas Pliers
- Brake Spring Pliers
- Battery Pliers
- Oil Filter Pliers
- Hog Ring Pliers
- Pump Pliers
- Grommet Pliers
- Fishing Pliers
- Duckbill Pliers
- End Cutting Pliers (Nippers)
- Hose Clamp Pliers
- Ear Clamp Pliers
- Nail Puller Pliers
- Safety Wire Pliers
- Spark Plug Pliers
- Packing Strap Pliers
- Bike Tire Pliers
- Wheel Weight Pliers
- Circle Nose Pliers
- Glass Grozing Pliers
- Breaker Grozer Pliers
In the following sections, we’ll explore some of the most common types of pliers, their designs, and common applications.
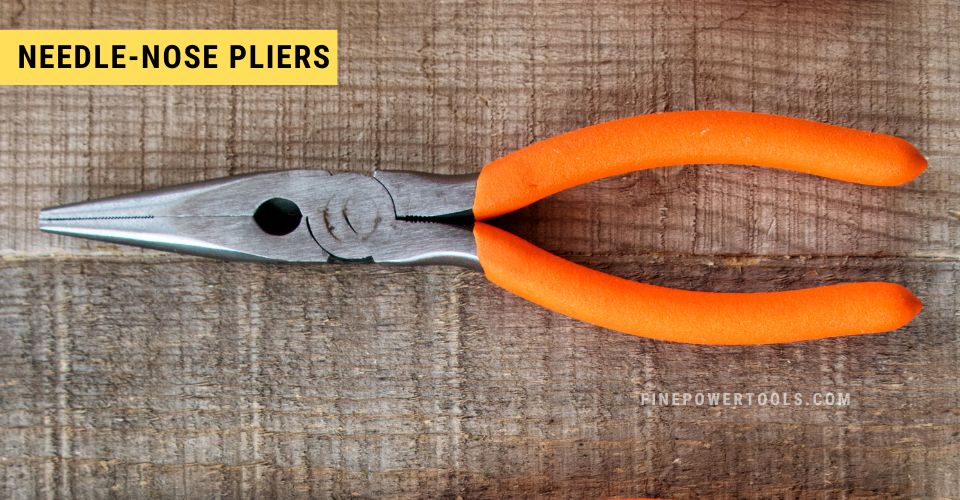
1. Needle-Nose Pliers
One of the most popular types of pliers, the needle-nose versions are distinctive thanks to their jaws, which taper down almost to a point at the end, hence the name. The jaws of needle-nose pliers tend to be longer and thinner compared to standard versions.

Uses:
Needle-nose pliers are designed for delicate work, especially in smaller spaces where standard pliers are unusable. You can use them to bend wires, put fasteners in place, and even cut wires or smaller objects thanks to the blades that are built-in to the pliers.
Despite their relatively small size compared to most other pliers, needle-nose pliers may be the most versatile of all pliers available.
2. Round-Nose Pliers
Round-nose pliers stand out in the tool family with their distinctive, fully rounded jaws, designed for precision tasks like forming loops and curves in wire.

Ideal for intricate jewelry-making, these pliers allow artisans to shape metal without marring the surface, preserving the finish of delicate pieces. While most models feature two rounded jaws, variations include a flat jaw for enhanced grip on flat objects.
Although their grip is less forceful compared to flat-jawed counterparts, round-nose pliers excel in applications where the cosmetic finish of the work is critical.
3. Diagonal Pliers (Side Cutters)
Diagonal pliers, commonly known as side cutters, are akin to scissors for robust materials like wires and soft metals. Their induction-hardened cutting edges ensure durability and a sharp, clean cut.
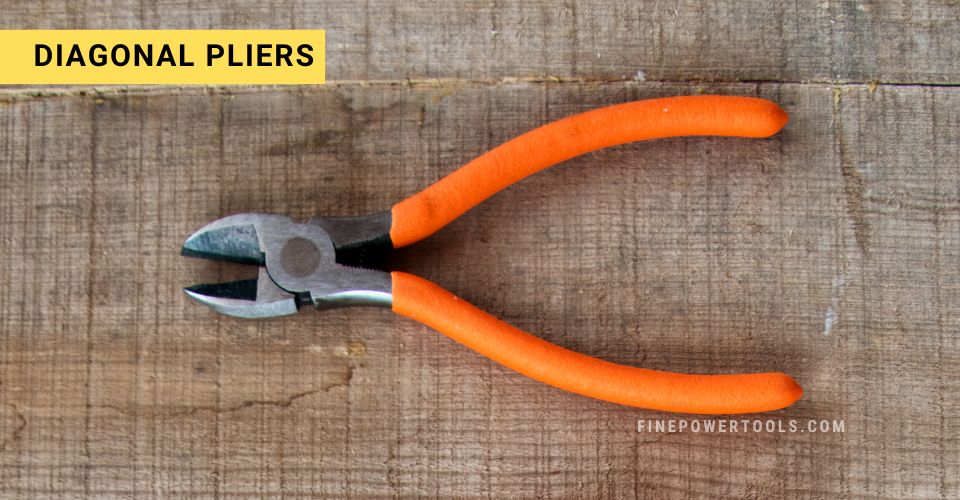

Designed specifically for cutting rather than holding, these pliers are indispensable to electricians for slicing through wires and cable ties, and they’re equally adept at trimming spring wire and other tough materials.
Uses:
Diagonal pliers excel at cutting wires, a task that endears them to electricians.
They’re also the tool of choice for snipping cable ties and removing excess wire. However, it’s important to use them solely for cutting; their sharp edges aren’t meant for gripping or twisting, as doing so can damage both the tool and the workpiece.
For safety and maintenance of the pliers, avoid cutting hardened steel or nails and always wear eye protection during use.
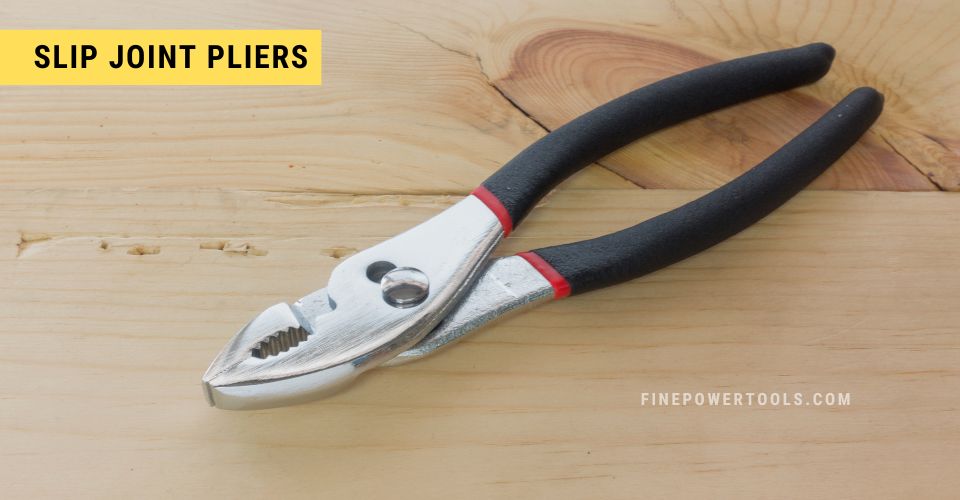
4. Slip Joint Pliers
Slip joint pliers are named for their distinctive adjustable mechanism—a slip joint—replacing a fixed pivot point. This allows you to move the pivot point effectively increasing the range of object size that the plier can grip.
This ability to adjust the jaw size makes it a versatile plier.

Uses:
As all-purpose tools, slip joint pliers excel at gripping, bending, crimping, and holding a diverse array of items. They can loop and cut wire, handle soft nails, and even adjust nuts within their capacity.
The tool has serrated jaws, which provide a firm grip, making it a useful tool for plumbing and general repair works.
Although tools like the Channellock and Pliers wrench can accommodate larger rage, slip joint pliers are useful in various situations.
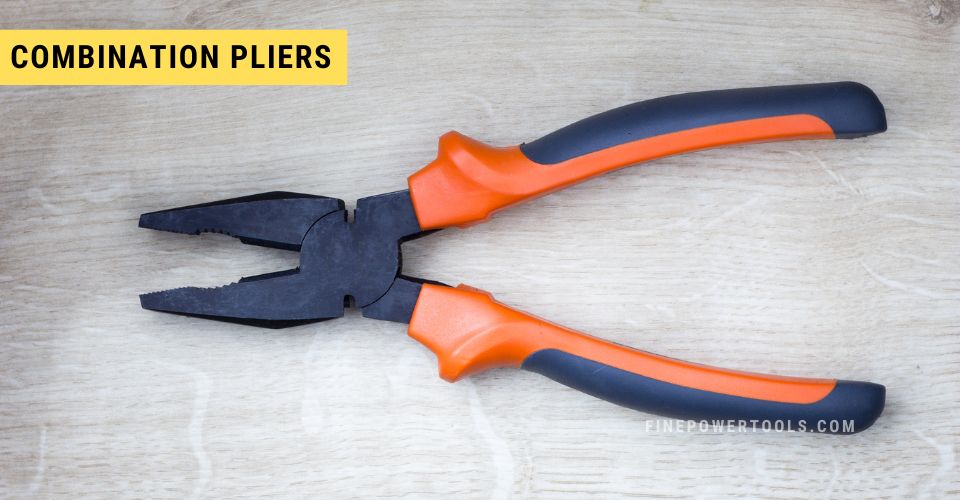
5. Combination Pliers
Combination pliers, perhaps the most commonly recognized pliers, is popular among home users as well as professionals.

Design:
The combination pliers have a multi-functional design with features that allow for gripping, bending, and cutting, making them an all-in-one tool for various applications.
Their distinctive design includes a broad gripping area with serrated jaws for a secure hold, a rounded outer edge for bending and looping wire, and a hardened cutting edge near the base for slicing through the wire with ease.
These tools often have a broad nose for a strong grip and sometimes additional features like crimping abilities, making them exceptionally handy for a wide array of DIY tasks.
Combination Pliers Uses:
These pliers are particularly useful for tasks that require both a firm grip and the ability to cut wire, such as electrical work, where their integrated cutting blades and gripping surfaces make them highly useful.
The versatility of combination pliers, with their ability to perform multiple tasks without the need to switch tools, explains their popularity in household toolboxes.
6. Lineman’s Pliers
Often referred to as electrician’s pliers, Lineman’s pliers are easily recognized by their sturdy construction, flat noses, and serrated jaws that provide a firm grip.
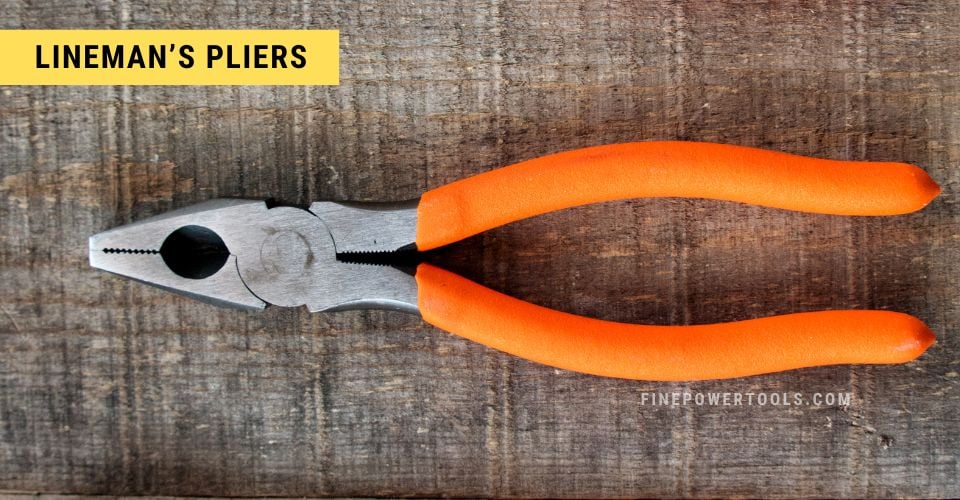

Design & Purpose:
Designed to grip and manipulate flat objects, these pliers are also adept at cutting and twisting wires, thanks to their side cutter blades and robust jaws. The serrated grip ensures a secure hold on objects, making them an indispensable tool in addition to wire strippers.
Their forged steel construction increases the durability while the built-in cutter is highly useful.
While many Lineman’s pliers feature dipped or insulated handles for added comfort and some electrical protection, caution should be exercised as they are not intended for live electrical work unless specifically certified for that purpose.
Lineman’s Pliers vs. Combination Pliers
Combination pliers have multi-functional jaws for gripping and stripping wires, and some also have crimpers. But the biggest difference is the serrated concave section on the jaws that can grip nuts, bolts, round shafts and pipes.
Lineman’s pliers feature knurled jaws and cutters for heavy-duty electrical work. They are larger, heavier and are capable of cutting larger diameter wires.
In US, we prefer lineman’s pliers, while Europe leans towards combination pliers.
The distinction between Lineman’s and Combination pliers lies in their design focus: Lineman’s pliers are built for strength and durability in demanding electrical work, whereas Combination pliers are more versatile.
7. Bent Nose Pliers
Bent-nose pliers, while functioning similarly to standard pliers, feature a distinctive angled tip that enhances their utility in various applications.
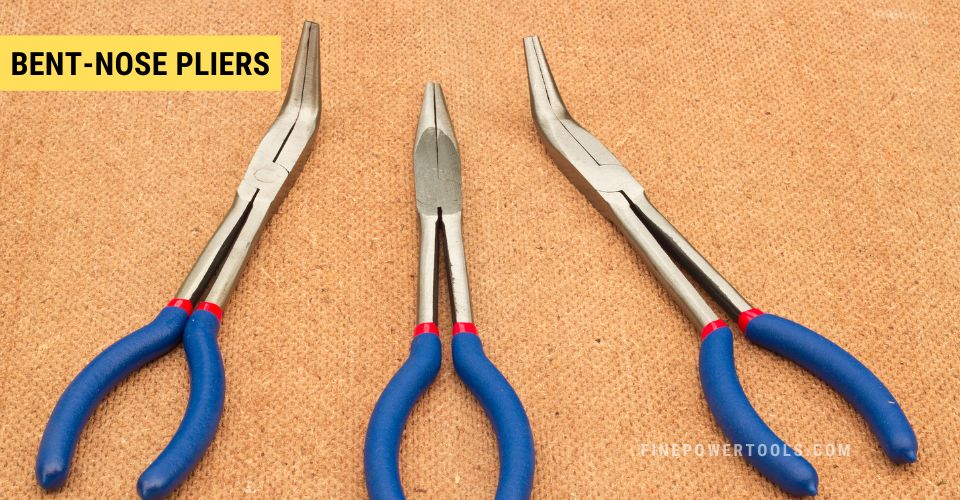

Design:
The tip, typically bent at a 45-degree angle, allows for improved access to confined spaces and provides an ergonomic advantage when manipulating small components. This design is particularly beneficial for intricate tasks where precision is paramount, and straight pliers would be cumbersome.
Uses:
These pliers are handy in electronics and jewelry-making, where you often need to place small parts precisely. The angled tips offer a clear line of sight and greater control, which is essential when working with delicate wiring or setting tiny stones.
In a household context, bent nose pliers are excellent for reaching into tight spots to retrieve or position small objects like springs, pins, or hooks that are otherwise difficult to manipulate with fingers or straight pliers.
Though they may not be as common in a basic home toolkit, they can be a useful tool if you are into jewelry making, electronics projects, etc.
8. Locking Pliers
Sometimes called vice grips, locking pliers are designed to clamp on objects and stay in place even when your hands are removed.
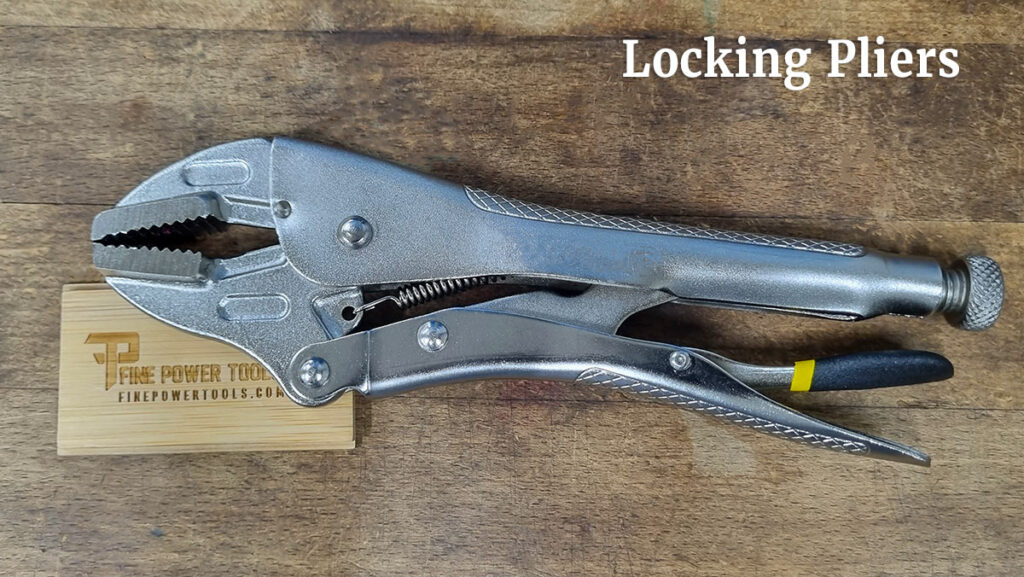

Design:
Locking pliers have a distinctive appearance, featuring an adjustable screw near the base of the handle that controls the width of the jaws. The jaws themselves often have a curved or straight design with serrated edges for a secure grip.
A distinct feature of locking pliers is the lever mechanism, usually located on the lower handle, which locks the pliers onto an object. The handles are typically forged to be parallel and may include a release lever that quickly disengages the locking mechanism.
How Does it Work?
The double-action lever mechanism lets the pliers tightly grip and lock onto an object, functioning similarly to a handheld vise.
Adjusting the screw at the end of the handle sets the jaw capacity and clamping pressure, allowing for a customized and secure hold on various objects.
Uses:
Locking pliers have a strong grip and can hold a diverse array of items securely in place. They are particularly useful for stabilizing a nut or bolt while adjustments are made on the opposite side. Given their ability to maintain a firm grip without continuous pressure from the user, this is a convenient tool for professional work and home garages.
9. Tongue-and-Groove (Channellock) Pliers
Also known as Channellock Pliers, after the popular brand, or water-pump pliers, these tools are a staple in many toolboxes due to their adaptability and robust design.
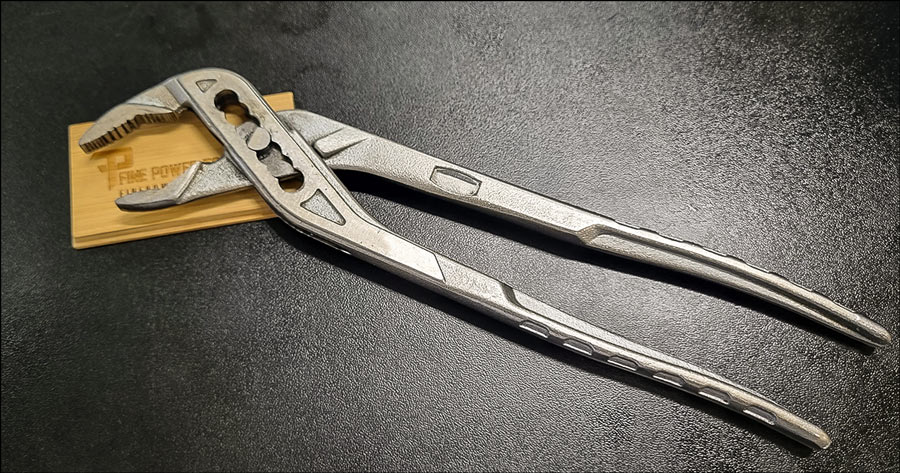

Design:
Tongue-and-groove pliers are characterized by their long handles and serrated jaws, which are designed to grip round, flat, or irregularly shaped objects. The jaws are set on a pivot with multiple grooves, allowing the user to adjust the span width to accommodate various sizes. This design provides a firm grip with significant leverage, making them ideal for tasks that require a strong, steady hold.
Uses:
While their primary use is in plumbing, for gripping and turning pipes, their utility extends to any situation requiring a secure grip, such as oil filter removal, opening stubborn jar lids, or holding objects steady for precision work.
The design allows for a ratcheting action, making them particularly effective for tasks that require repetitive adjustment or holding power.
10. Pliers Wrench
Pliers wrenches ingeniously merge the gripping power of tongue-and-groove pliers with the versatility of an adjustable wrench, creating a multi-purpose tool that excels in precision and adaptability.
Design:
The defining feature of Pliers Wrench is its smooth, parallel jaws, which avoid damaging the workpiece, paired with a convenient push-button adjustment that provides quick and precise sizing. Their slim profile and high-leverage design enable both a strong grip and the ability to apply significant turning force.
Uses:
Ideal for delicate surfaces where a soft touch is needed, pliers wrenches can grip, bend, and twist without marring. They are equally adept at securely holding various shapes and sizes, as well as functioning as an adjustable wrench for tightening or loosening nuts and bolts.
Their dual functionality makes them particularly valuable in fields requiring fine adjustment and care, such as in plumbing, electrical, and finish carpentry.
While their dual nature may not replace the need for a full set of pliers and wrenches in a household, for those with limited space or the need for a versatile, on-the-go tool, pliers wrenches are an excellent compromise.
11. Wire Stripping Pliers
Wire strippers are essential when you need to expose the conductive material of a wire for electrical or data connections. They’re designed to neatly remove the insulation without harming the wire itself, which is crucial for a safe and effective connection.
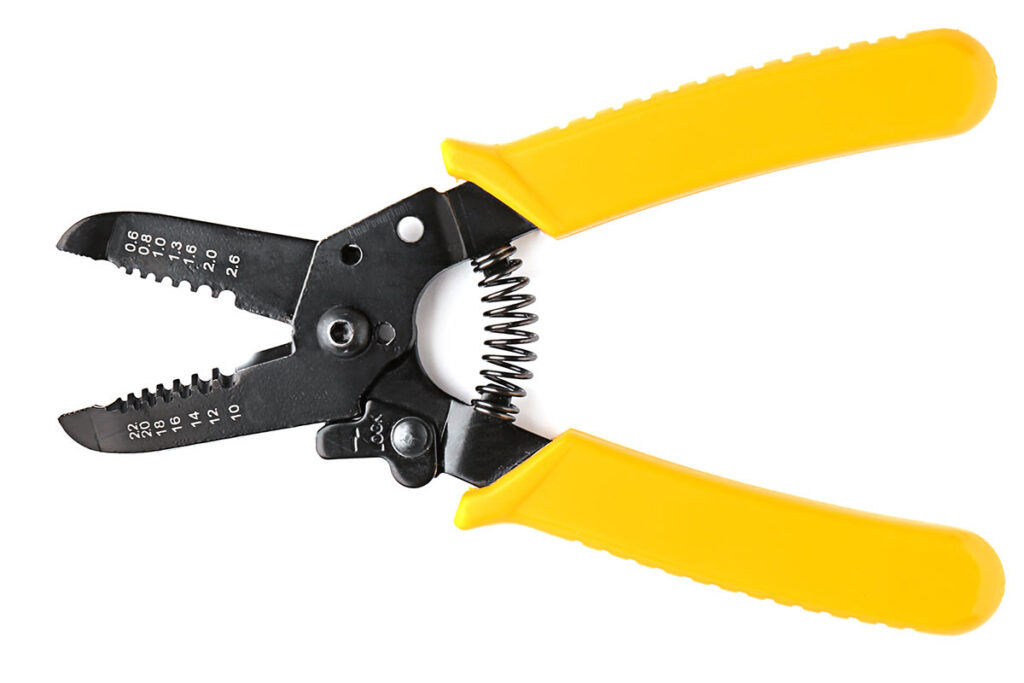

Design:
These pliers look like a pair of scissors with holes in their jaws. Each hole size corresponds to a different wire gauge.
Place the wire to the right notch, and squeeze the handle to cut the insulation around the wire cleanly. This design ensures you don’t accidentally cut into the wire itself, which could cause problems when you’re making connections.
They come in different sizes and models. Check the articles on different types of wire strippers and how to use them written by David.
Uses:
Wire strippers are used anytime you need to connect wires to terminals, join them together, or attach them to various devices. They’re a go-to tool for electricians and DIY enthusiasts alike when preparing wires for crimping, soldering, or creating secure electrical joints.
Whether you’re installing a new light fixture or setting up a sound system, these pliers help you safely prepare the wires for a reliable setup.
12. Crimping Pliers
Crimping pliers are specialized tools designed for holding and joining materials with a crimped seal that ensures a strong, secure connection.
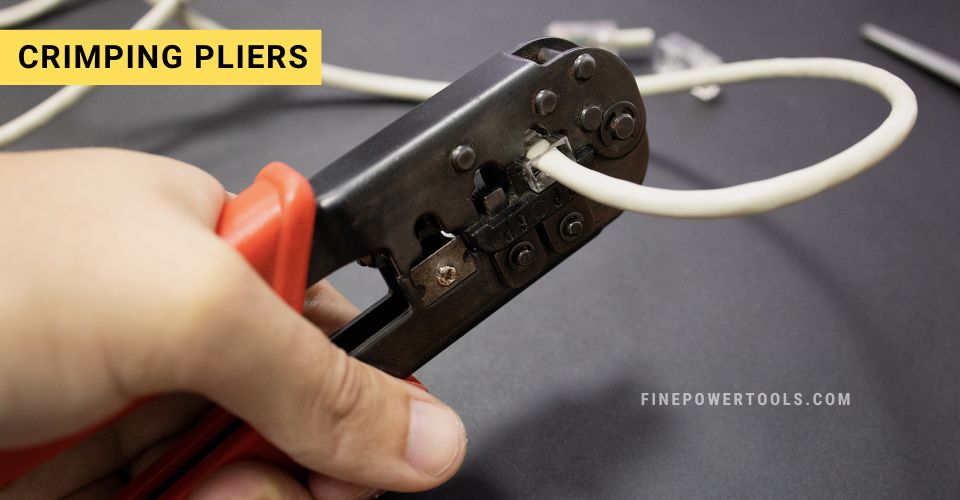

Design and Working:
These pliers feature a distinctive, wide jaw with a series of notches or crimps of varying sizes, catering to different types and sizes of connectors.
The jaws are typically not meant for wide opening; rather, they are precision-engineered to deliver a concentrated crimping force to secure a connector to a wire.
Uses:
Essential for electricians, crimping pliers are used to affix various types of connectors onto electrical cables and wires with reliability and ease. They are indispensable for creating seamless connections in telecommunications, networking, and audio-video wiring, where a stable connection is critical.
The ability to crimp, cut, and strip wires makes them a multifunctional tool for wiring tasks that require precision and durability.
13. Snap Ring Pliers (Circlip Pliers)
Circlip pliers, also known as snap ring pliers, are specialized tools designed for a singular purpose: the precise handling of circlips, which are a type of fastener used to secure components on shafts or within bores.
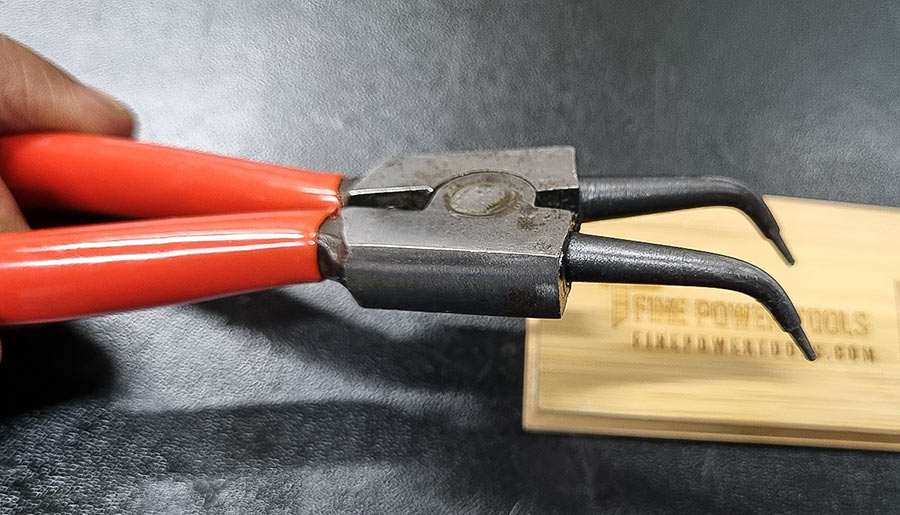

Design:
These pliers are characterized by their small, notched tips, which are designed to fit into the holes of circlips, providing the leverage needed for installation or removal.
The fixed pivot point provides stability, while the tips are often interchangeable to accommodate various sizes and types of circlips.
Uses:
Circlip pliers are essential in automotive and machinery maintenance for installing or removing circlips that hold bearings, gears, and other components in place.
They come in both straight and angled varieties, the latter of which is particularly useful for working in confined spaces. While not a common household tool, they are indispensable in workshops and for those performing mechanical repairs.
14. Fencing Pliers
A fencing plier is a specialized hand tool used for installing and repairing barbed wire fencing.
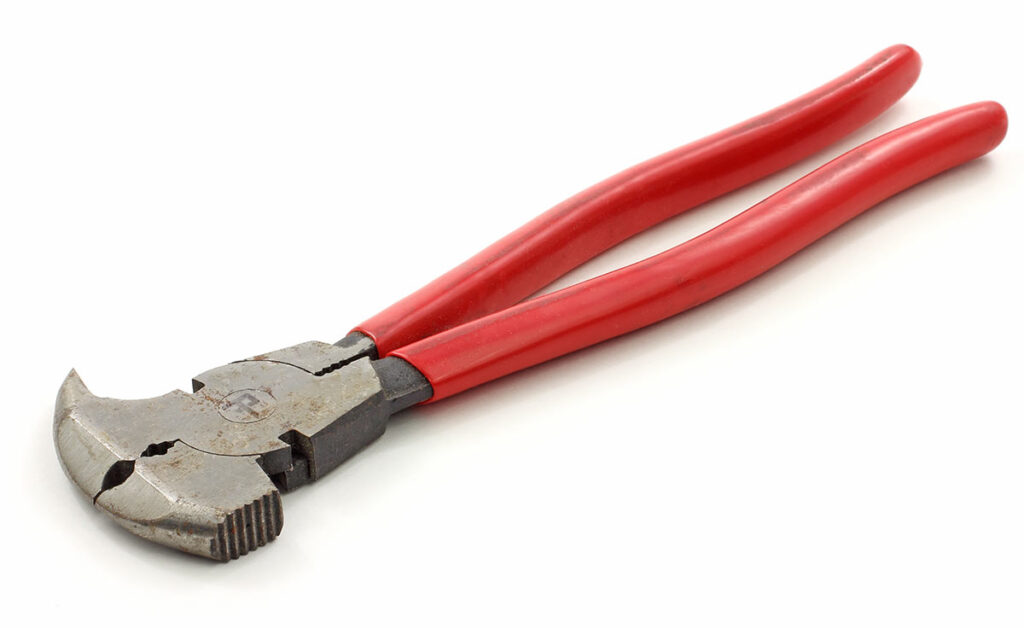
Design:
Arguably the most unusual-looking set of pliers you may ever see, fencing pliers are noted for their long handles, hammer-head shape, large pivot, and relatively small opening for the jaws.
The jaws, often compact, are adept at gripping and twisting wire, with integrated cutters near the pivot for snipping duties.
Uses:
Their versatility makes them indispensable on the ranch or farm, capable of cutting, twisting, and gripping wire, as well as hammering and removing staples.
Despite their specialized design, they are less likely to be found in a typical homeowner’s toolbox, as their functions are tailored more towards agricultural fencing rather than everyday DIY tasks.
15. Wire-Twisting Pliers
Wire-twisting pliers are a specialty item that, as the name suggests, are designed to twist wires together so they remain connected.
Design and Working:
These pliers typically feature a return spring and a locking mechanism, which contributes to their ergonomic build, reducing hand fatigue during repetitive use. Although standard pliers can also twist wiring, this design is optimized to apply consistent force, which is essential for creating consistent wire twists.
Uses:
Wire-twisting pliers are primarily used in industries such as electronics, automotive, and jewelry.
This type of pliers come in various sizes but are adjustable, making them easy to use. Plus, their ergonomic design and application of force make them a suitable alternative to using power tools for twisting wires.
Back to Contents
- List of Pliers
- 1. Needle-Nose Pliers
- 2. Round-Nose Pliers
- 3. Diagonal Pliers (Side Cutters)
- 4. Slip Joint Pliers
- 5. Combination Pliers
- 6. Lineman’s Pliers
- 7. Bent Nose Pliers
- 8. Locking Pliers
- 9. Tongue-and-Groove (Channellock) Pliers
- 10. Pliers Wrench
- 11. Wire Stripping Pliers
- 12. Crimping Pliers
- 13. Snap Ring Pliers (Circlip Pliers)
- 14. Fencing Pliers
- 15. Wire-Twisting Pliers



